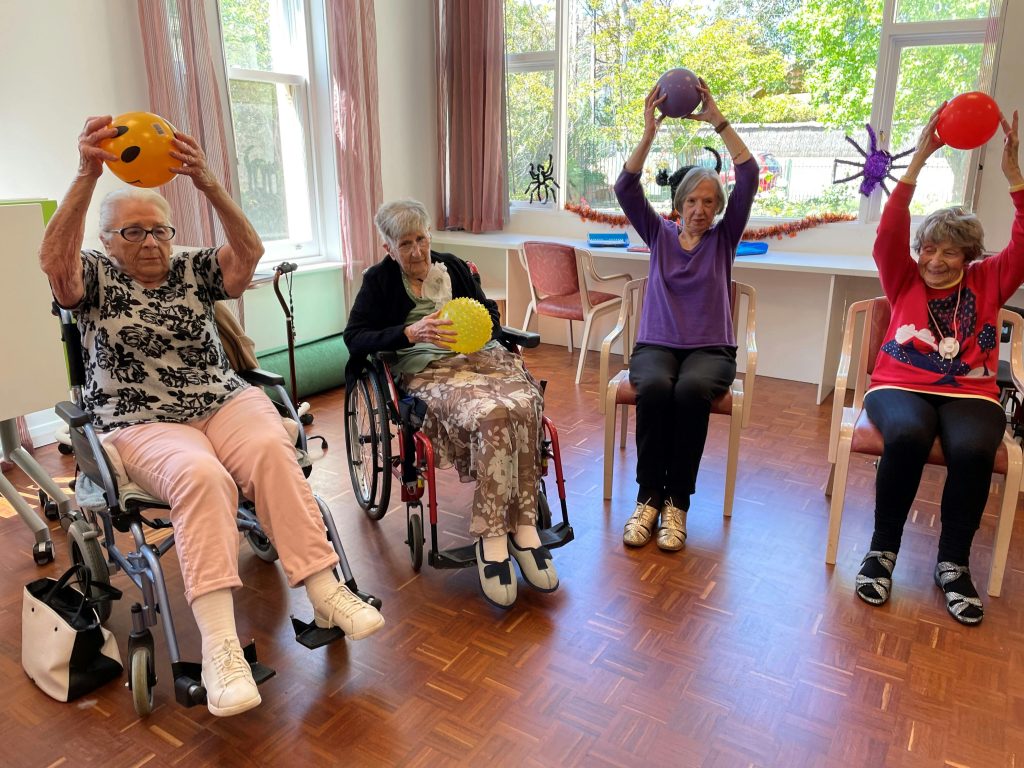Falls are a significant concern in residential settings, particularly in facilities housing elderly individuals. Preventing falls not only enhances resident safety but also improves their overall quality of life. Implementing effective fall prevention measures requires a comprehensive and systematic approach.
Understanding Fall Risks
Common Causes of Falls
- Environmental Hazards: Poor lighting, slippery floors, uneven surfaces, and clutter can all contribute to falls.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like osteoporosis, arthritis, and vision impairment increase fall risk.
- Medications: Some medications can cause dizziness or balance issues.
- Mobility Issues: Muscle weakness, balance disorders, and gait problems.
- Behavioral Factors: Risky behaviors such as rushing, improper use of mobility aids.
Risk Assessment
- Initial Assessment: Conduct thorough initial assessments for all residents, including medical history and mobility tests.
- Regular Monitoring: Implement regular reassessments to monitor any changes in a resident’s condition.
- Personalized Care Plans: Develop individualized care plans based on each resident’s specific risk factors.
Environmental Modifications
Indoor Environment
- Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting in all areas, especially in hallways, stairs, and bathrooms.
- Flooring: Use non-slip mats and rugs, and ensure floors are even and clean.
- Handrails and Grab Bars: Install handrails in corridors and grab bars in bathrooms.
- Furniture Arrangement: Arrange furniture to allow easy navigation and remove unnecessary obstacles.
Outdoor Environment
- Walkways: Maintain clear and even walkways, free of debris and clutter.
- Lighting: Adequate outdoor lighting for pathways and entrances.
- Stairs and Ramps: Ensure stairs have sturdy handrails and ramps are available for wheelchair access.
Medical and Health Interventions
Medication Management
- Review Medications: Regularly review resident medications with healthcare providers to minimize fall-risk medications.
- Adjust Dosages: Adjust dosages or switch medications if necessary to reduce side effects like dizziness.
Physical Health
- Exercise Programs: Implement regular exercise programs focusing on strength, balance, and flexibility.
- Physiotherapy: Provide access to physiotherapy for residents with significant mobility issues.
- Vision and Hearing: Regularly check and correct vision and hearing impairments.
Nutrition
- Balanced Diet: Ensure residents receive a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to maintain bone health.
- Hydration: Encourage proper hydration to prevent dizziness and confusion.
Training and Education
Staff Training
- Fall Prevention Training: Provide comprehensive training for staff on fall prevention strategies and proper response to falls.
- Emergency Procedures: Train staff in emergency procedures for handling fall incidents.
Resident Education
- Awareness Programs: Conduct regular awareness programs for residents about fall risks and prevention strategies.
- Safe Behavior: Educate residents on the importance of safe behavior, such as using mobility aids correctly and wearing proper footwear.
Family Involvement
- Communication: Maintain open communication with family members about fall risks and prevention measures.
- Involvement in Care Plans: Involve family members in the development and review of individualized care plans.
Technology and Monitoring
Assistive Devices
- Mobility Aids: Provide and maintain appropriate mobility aids such as walkers, canes, and wheelchairs.
- Fall Detection Devices: Utilize fall detection devices and alarms to alert staff in case of a fall.
Monitoring Systems
- CCTV: Install CCTV cameras in common areas to monitor resident movements.
- Wearable Devices: Use wearable devices that monitor vital signs and detect falls.
Policy and Procedure Development
Fall Prevention Policies
- Standardized Policies: Develop and implement standardized fall prevention policies.
- Incident Reporting: Establish a system for reporting and analyzing fall incidents to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of fall prevention measures and make necessary adjustments.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback mechanisms to gather input from staff, residents, and families on the effectiveness of fall prevention measures.
Conclusion
Implementing comprehensive fall prevention measures requires a multi-faceted approach that includes environmental modifications, medical and health interventions, training and education, technology, and robust policies. By addressing these areas thoroughly, residential facilities can significantly reduce the risk of falls and ensure the safety and well-being of their residents.